Research equipment

XR mobility platform
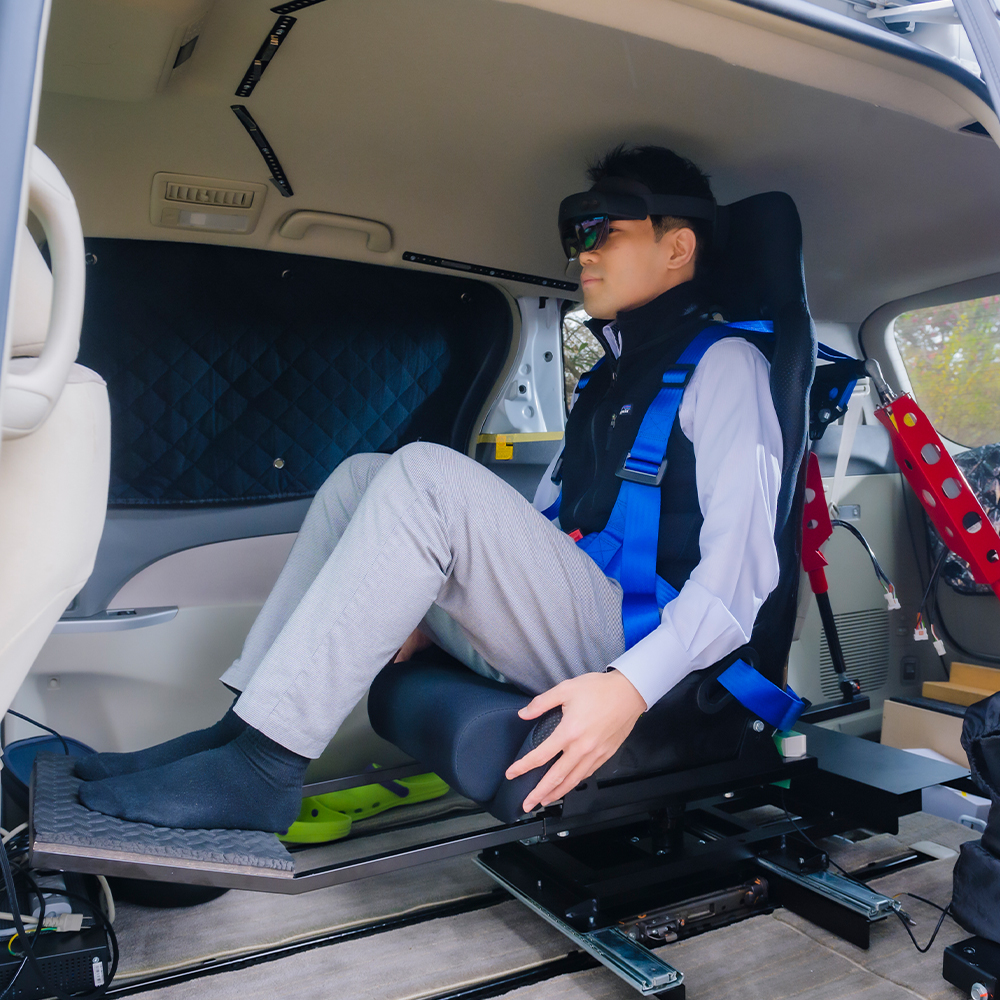

XR mobility platform is the platform that consists of an immersive VR and see-through AR information display system with a motion platform seat inside a fully autonomous vehicle. Outside view of the autonomous vehicle is a Minivan type with a Lidar scanner mounted on the top of the roof. The projection-based detachable cylindrical screen with a wide field of view or Head-Mounted Display (HMD) can be used as an immersive display to realize a high presence VR environment inside the autonomous vehicle. Moreover, the system has functions to make a video see-through AR environment by using projection-based display or HMD that displays images recorded by a dashboard camera. Additionally, the system also has functions to make an optical see-through AR environment by detaching the cylindrical screen and using an optical see-through HMD. Furthermore, a motion platform with the passenger seat is mounted at the backspace of the MiniVan that can control an angle of the tilt seat. The seat is only for a passenger, and multiple actuators are connected with the back of the seat to control tilt by a computer.
(Interactive Media Design)
Japanese Style Meeting Room, and IoT/server accelerated by FPGA
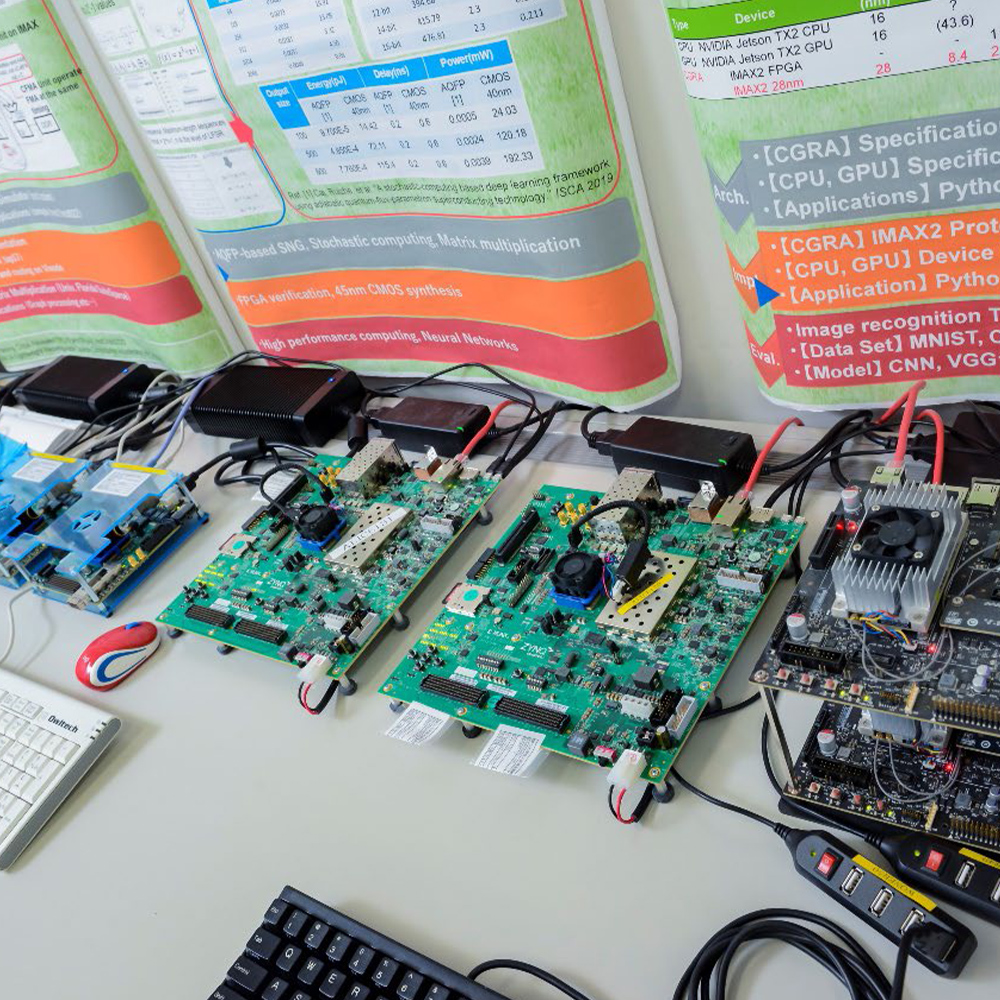


Series of large-scale FPGA systems on Intel/ARM servers are available. Linux/FreeBSD on Intel/ARM can send large data to FPGA through DMA/PCI interface so that large-scale data to be processed in high-speed on accelerators. Digital and stochastic computations are available.
(Computing Architecture)
Testbed for Neuromorphic Devices
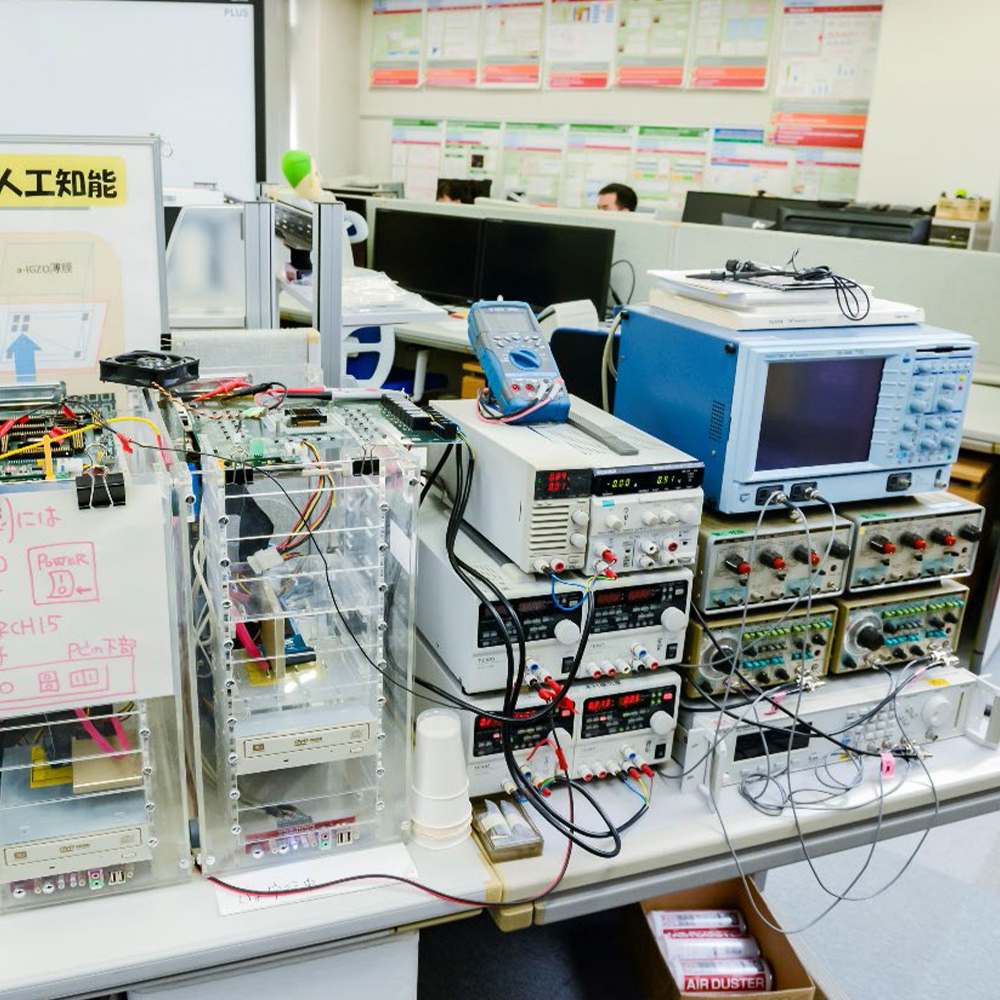

Environment for Neuromorphic LSI based on non-silicon material, and testbed for image recognition.
(Computing Architecture)
Next generation CGRA platform
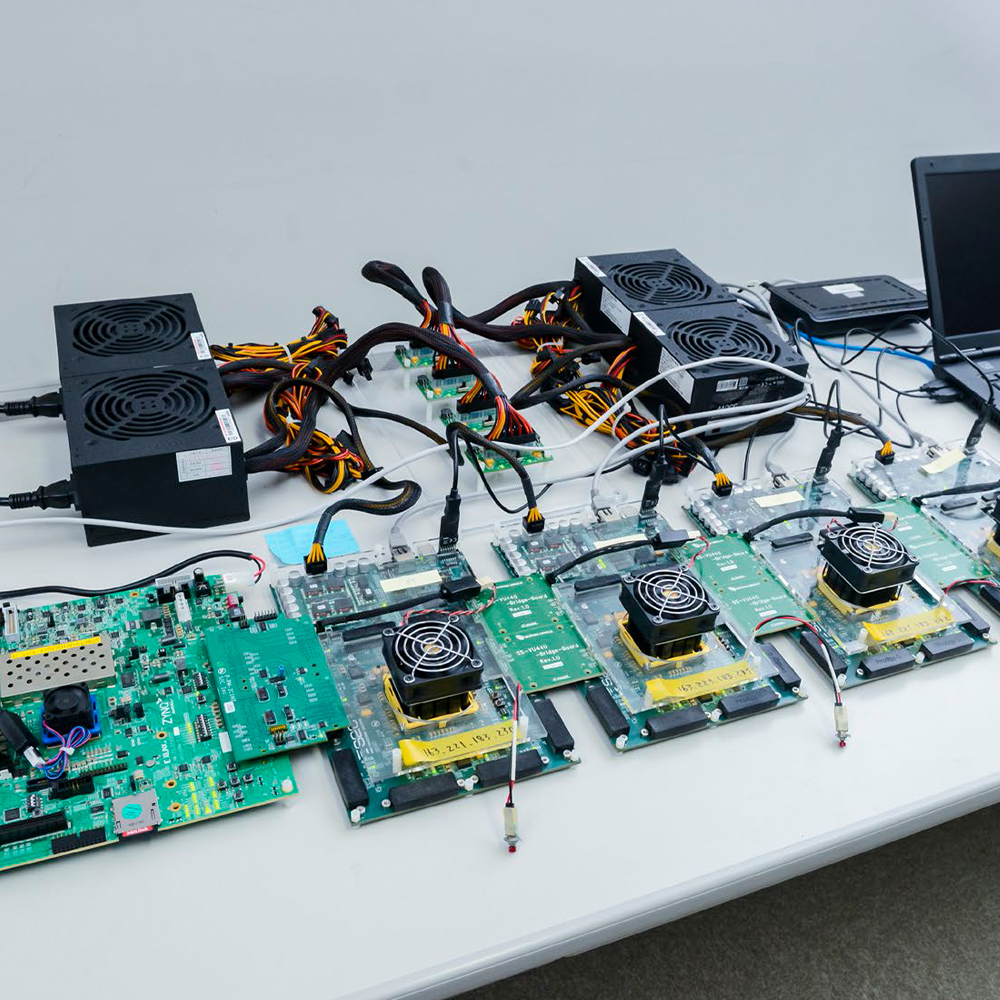
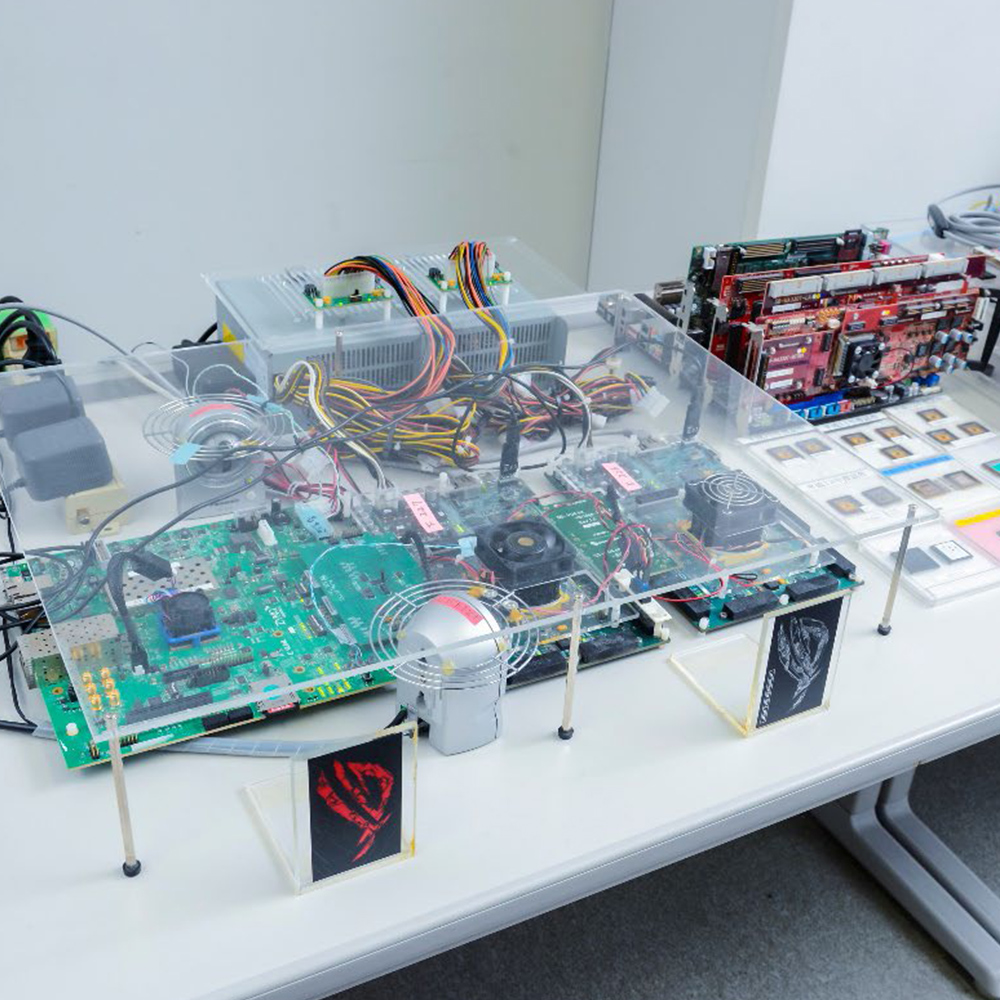


Real hardware of next generation CGRA (IMAX2: 1024 operations per 4 cycles). Sample programs, compiler, simulator, waveform capturing, and so on are available with source code (all of these are developed in the lab). The performance per memory bandwidth / area of IMAX2 are 100x / 200x compared to GPU.
(Computing Architecture)
FPGA, GPGPU servers, and Fugaku (8 nodes /384 cores)
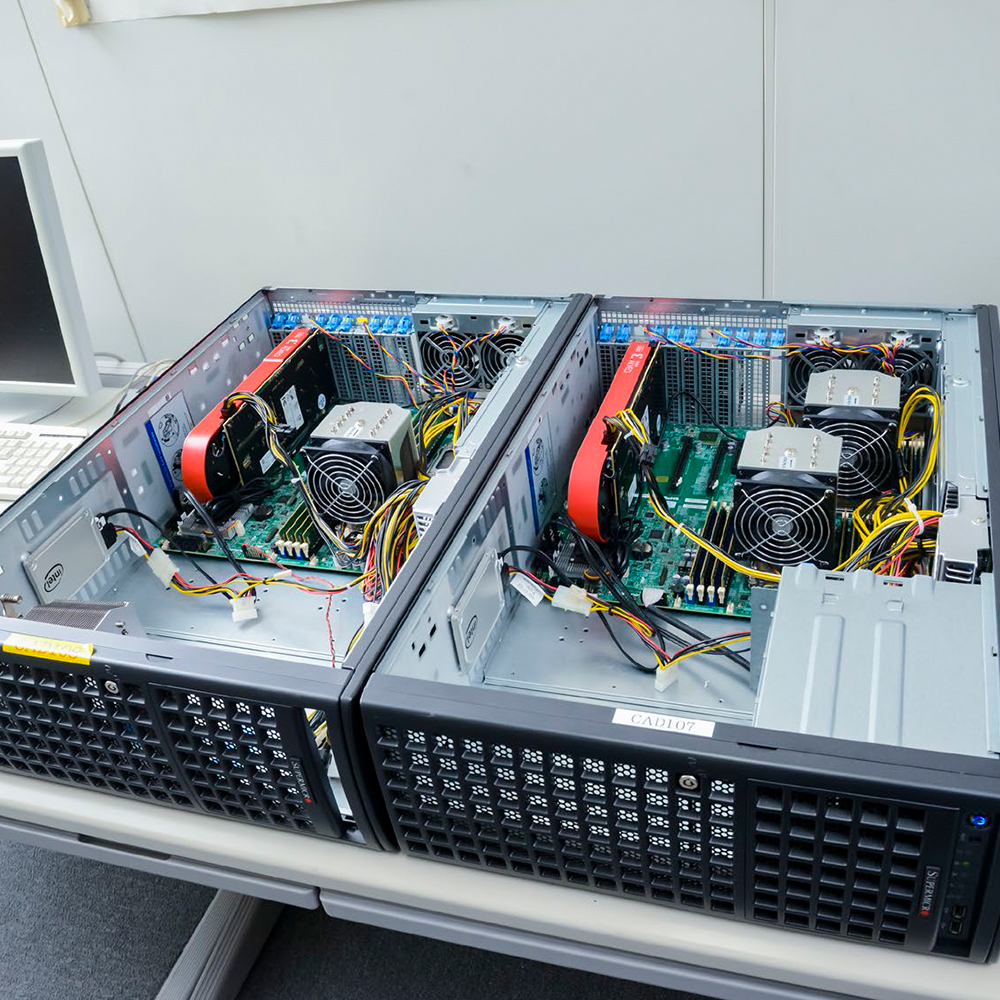


Can be occupied with no time limitation.
(Computing Architecture)
Electric vehicles for car-sharing experiments
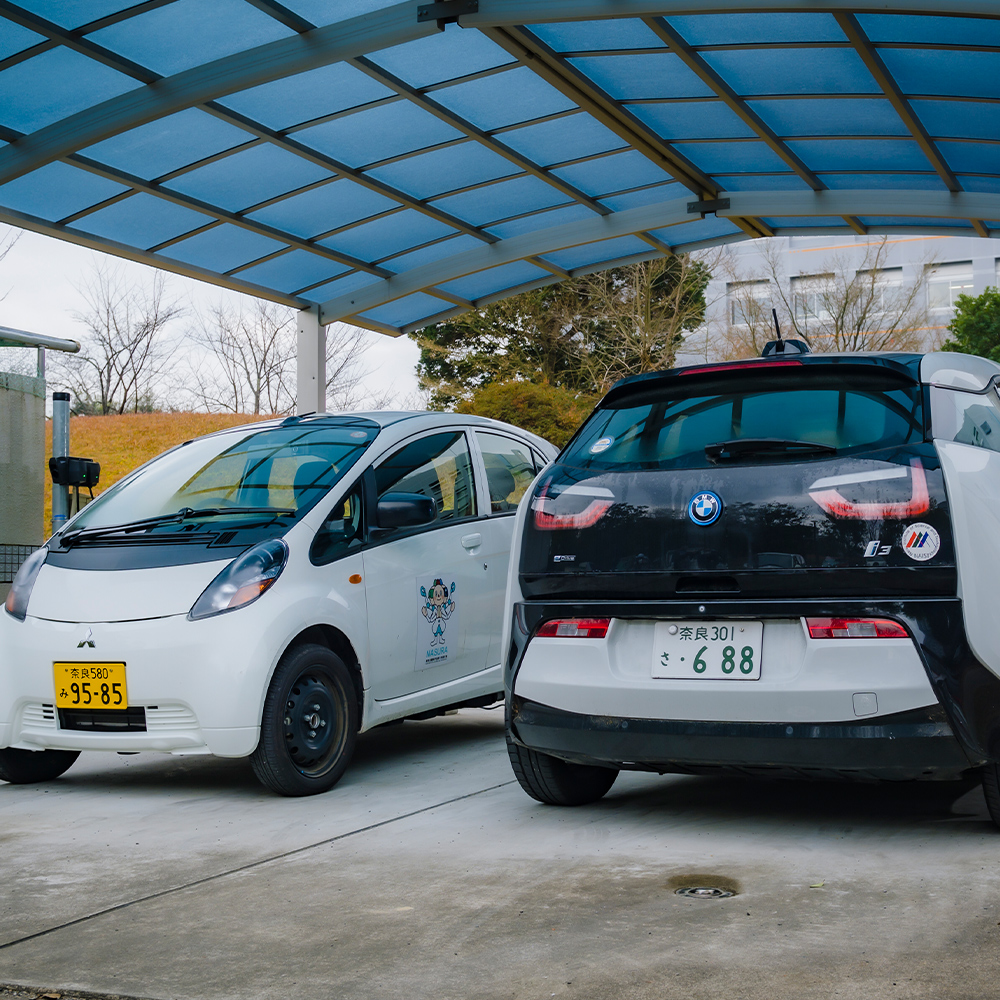

Experiments are being conducted on car sharing using these electric vehicles, in which users acquire usage rights through mobility auctions and leave their cars between designated stations.
(Software Engineering)
Software ecosystem archive server
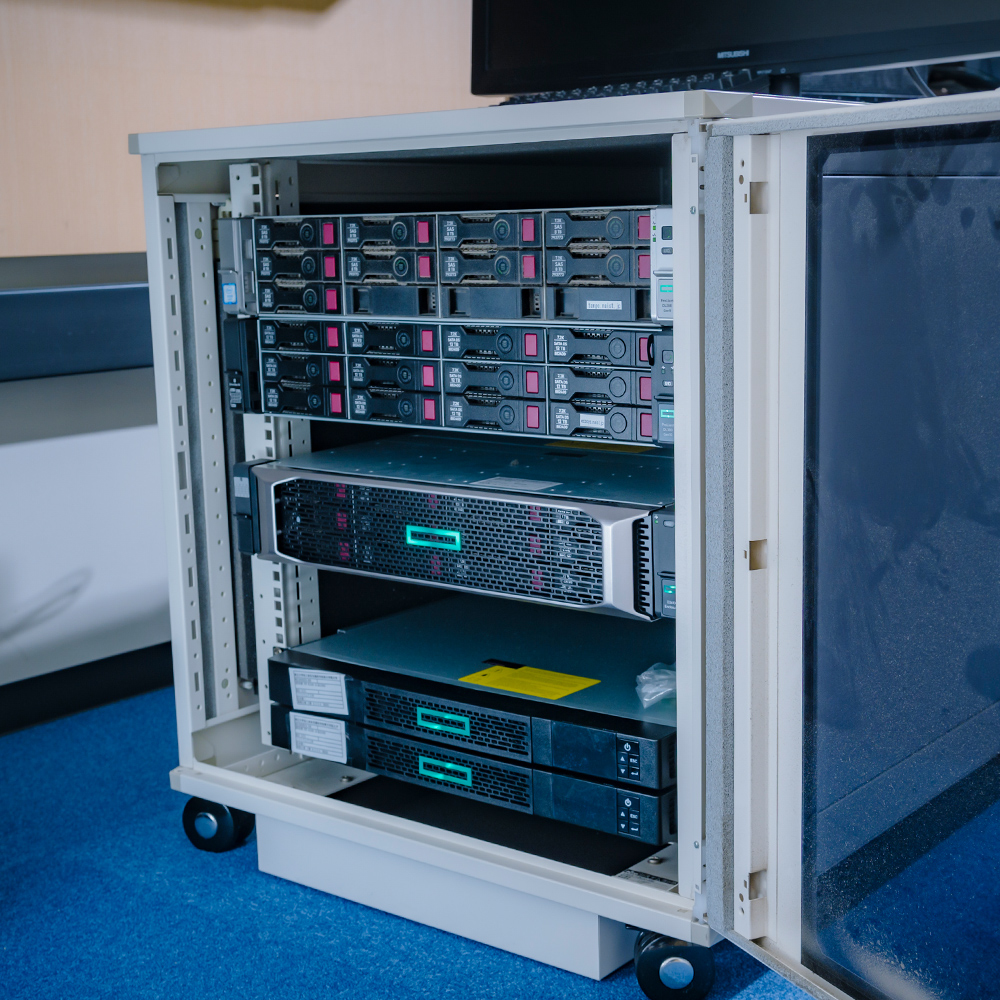

A storage server with 248 TB disks. It stores snapshots of the development history of more than 100,000 open source software projects on the Internet that have been used for analyzing activities of OSS developers.
(Software Engineering)
Cloud Computing Experimental System
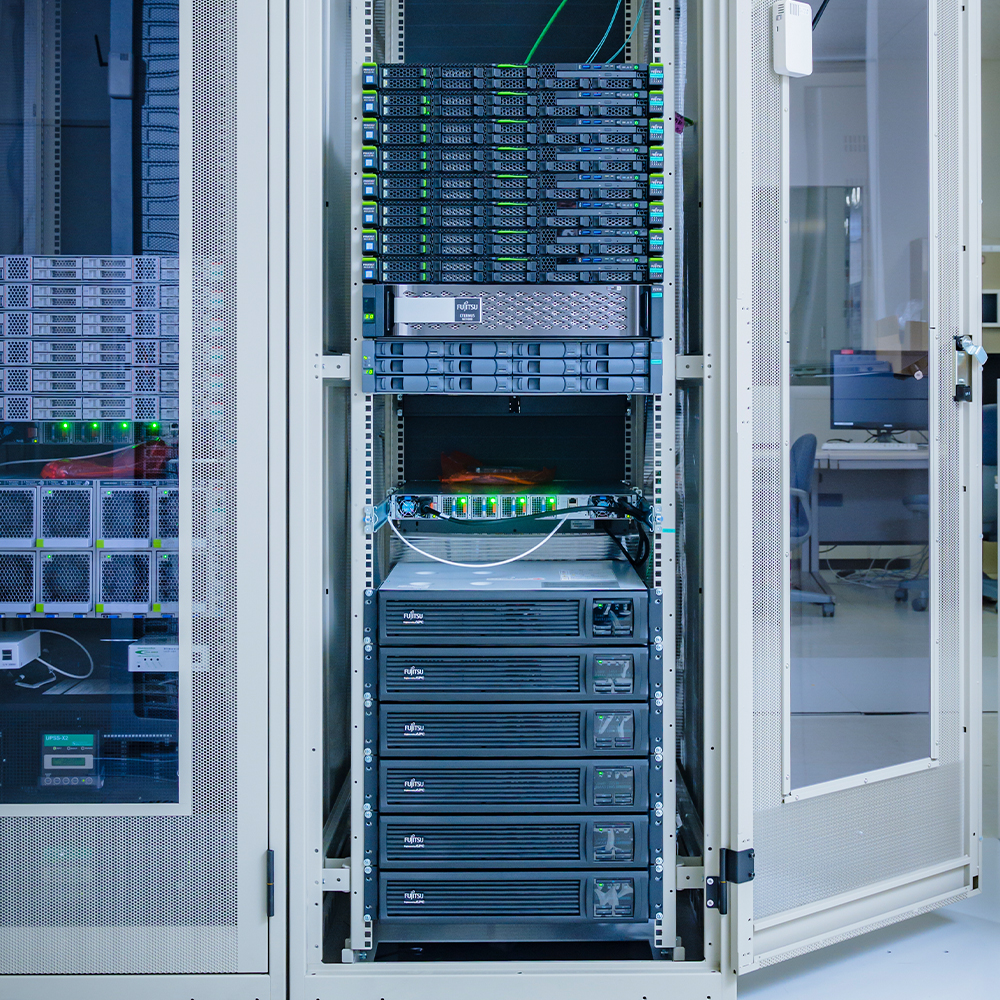

A private cloud system for cloud computing experiments and software data analysis. It integrates ultra-high-speed, high-reliability network storage with 47TiB of RAID6 HDDs and 2TiB of NVMe for cache, and servers with a total of 128 CPU cores and 576GiB of memory, using a virtualization platform vSphere.
(Software Design and Analysis)
Mobile Robots (Kilobot and Khepera IV)
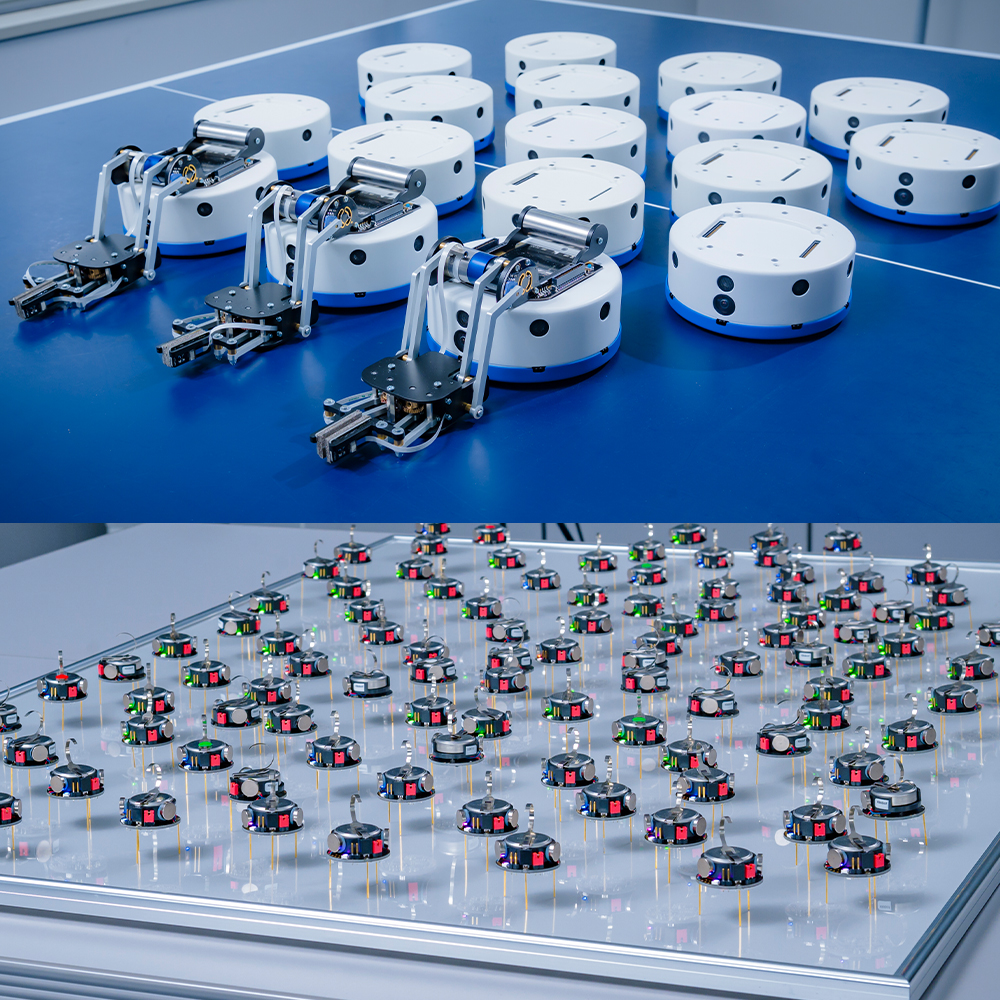

With 150 Kilbots and 18 Khepera IVs, we are developing distributed algorithms to cooperatively operate a swarm of robots. Kilbot is a very small (3.3cm) robot that can communicate with nearby Kilobots and move autonomously.Khepera IV is also a small (14cm) robot that can communicate and move.In addition, Khepera IV has many types of sensors (a color camera, infrared sensors, ultrasonic sensors, a microphone, an accelerometer, a gyroscope).
(Dependable System)
Smart Home Facility
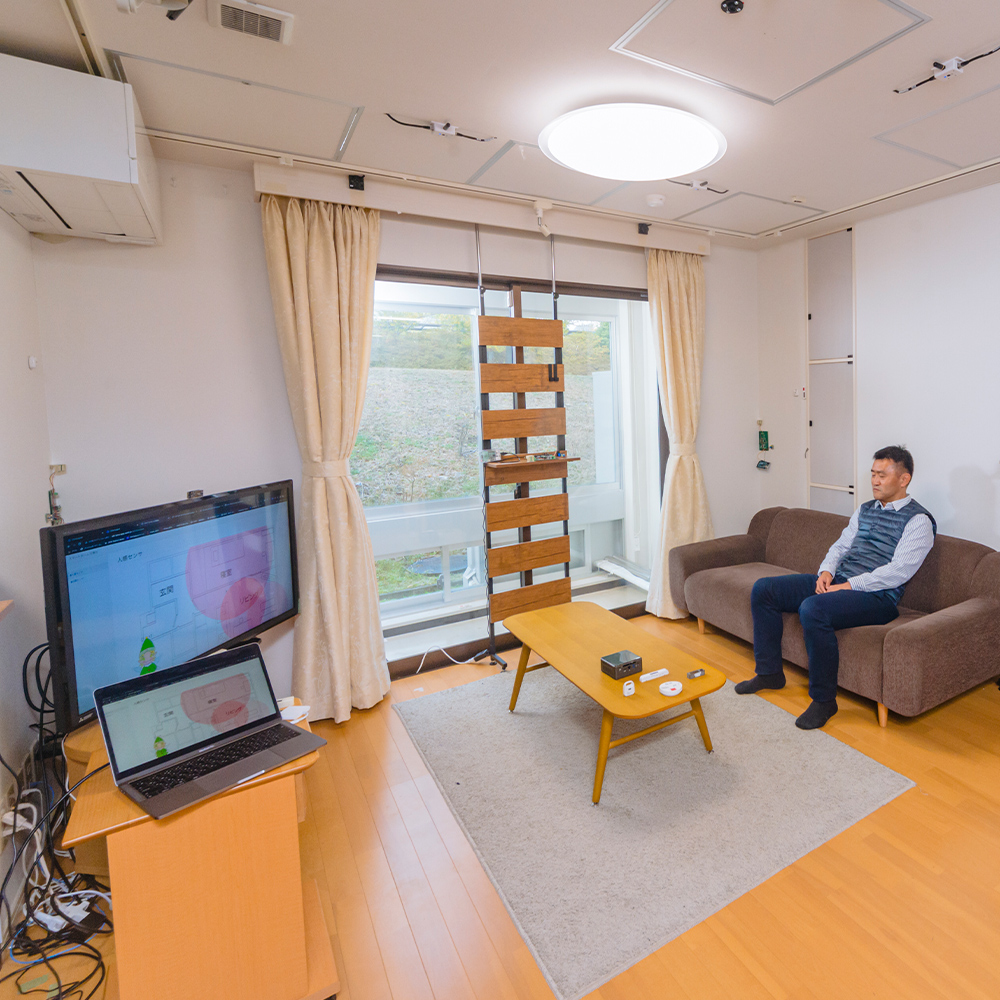
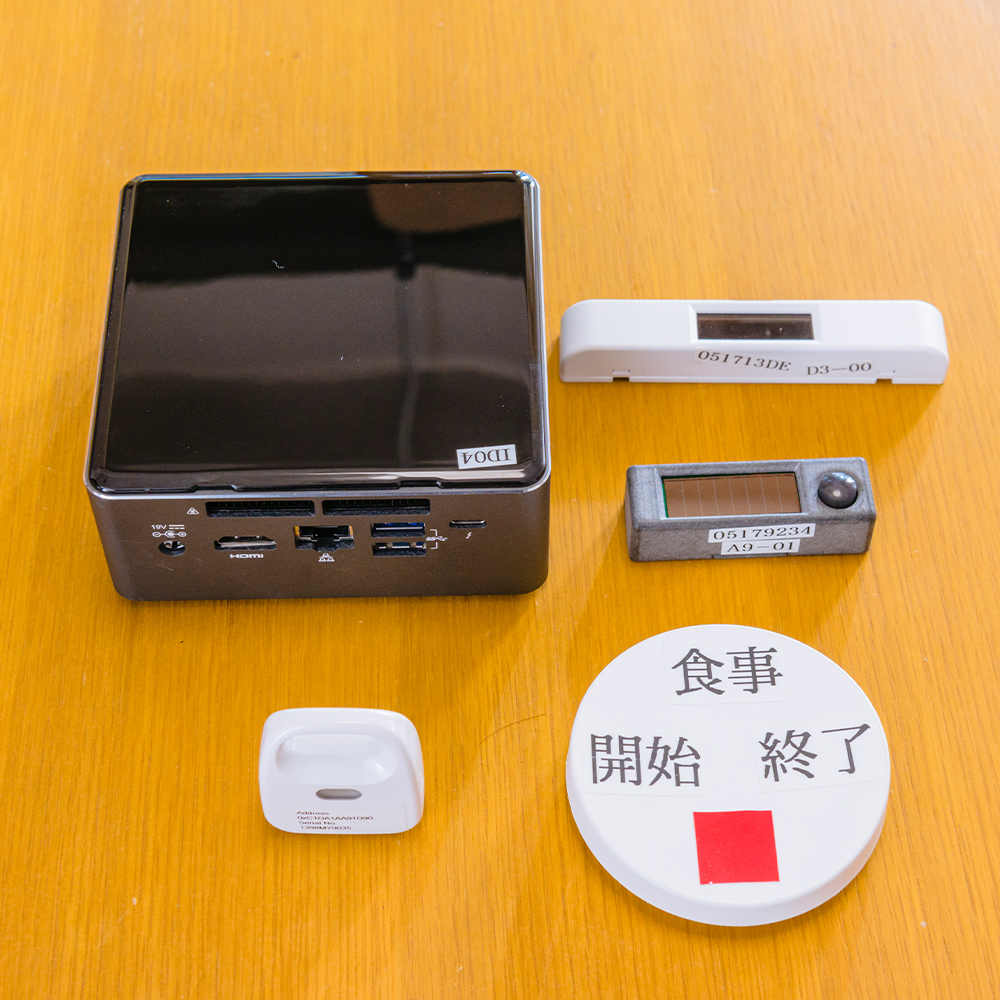


This facility provides, as a testbed, an actual home environment with a living room, a kitchen, a toilet, a bathroom, a bedroom, where various home appliances are deployed as in an ordinary household. In addition, this facility is equipped with special sensors including high-accuracy indoor positioning system, wireless power meters, door sensors, ambient sensor (temperature, humidity, illuminance, etc), and motion sensors. We are collecting data while subjects are actually living in this facility and are developing various methods including activity recognition and automatic appliance control using the collected sensor data.
(Ubiquitous Computing Systems)
Nextage Open
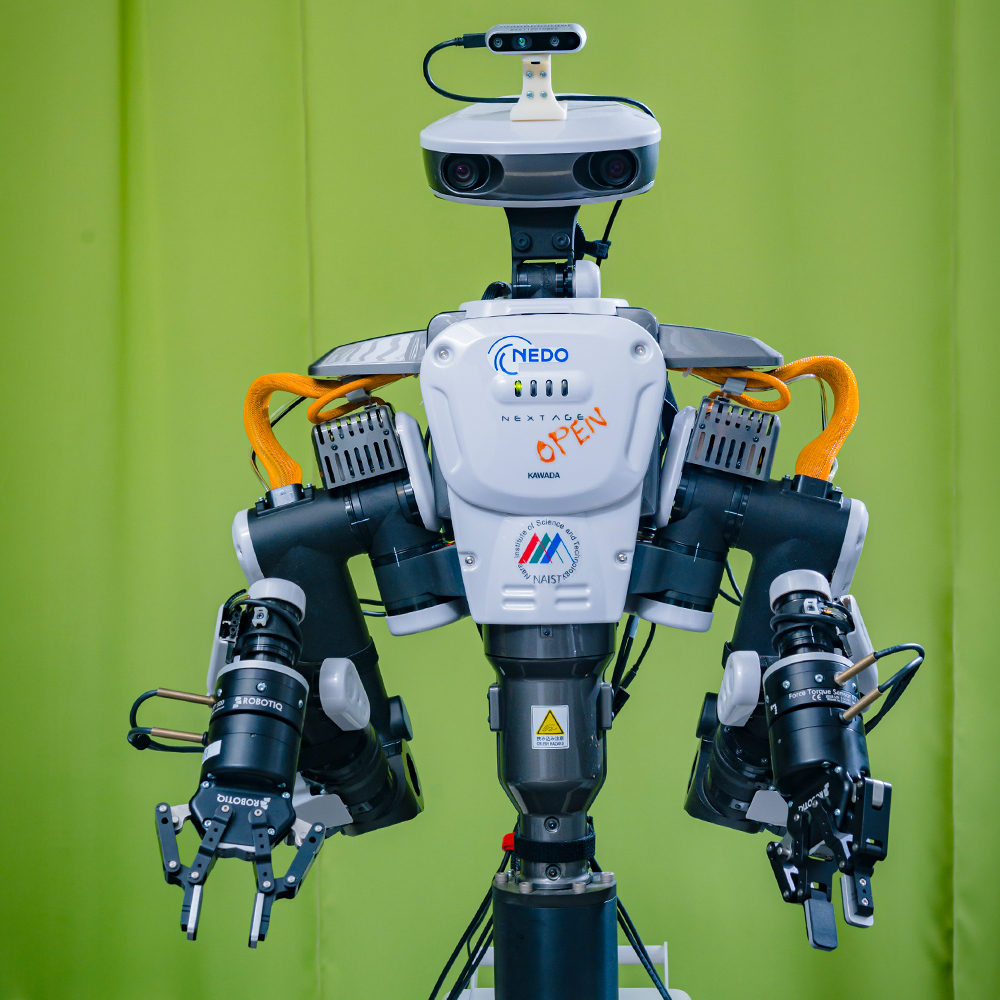

With versatile arms and precise movements, the Nextage robot (15 DoF, 6 for arms × 2, 2 for neck, 1 for waist) is able to achieve and even surpass the manufacturing ability of most humans. Thanks to its scalable open software environment (based on C++/Python/ROS) and functional body, the Nextage robot is a suitable investigation platform for learning control strategy using modern machine learning/reinforcement learning algorithm.
(Robot Learning)
Universal Robot 5 e-series (UR5e)
The UR5e robot has six-axis robot arm with a 5kg payload. Its repeatability is ± 0.03 mm, along with speeds up to 1 meter/sec allowing quick precision handling of even microscopically small parts. It has a great balance between control accuracy and velocity and therefore perfectly matches not only pick up/assembling tasks but also safe collaboration with humans. The UR5e robot supports both simple interactions using intuitive tablet interface and programming on scalable open software environment.
(Robot Learning)
Universal Robot 3 (UR3)
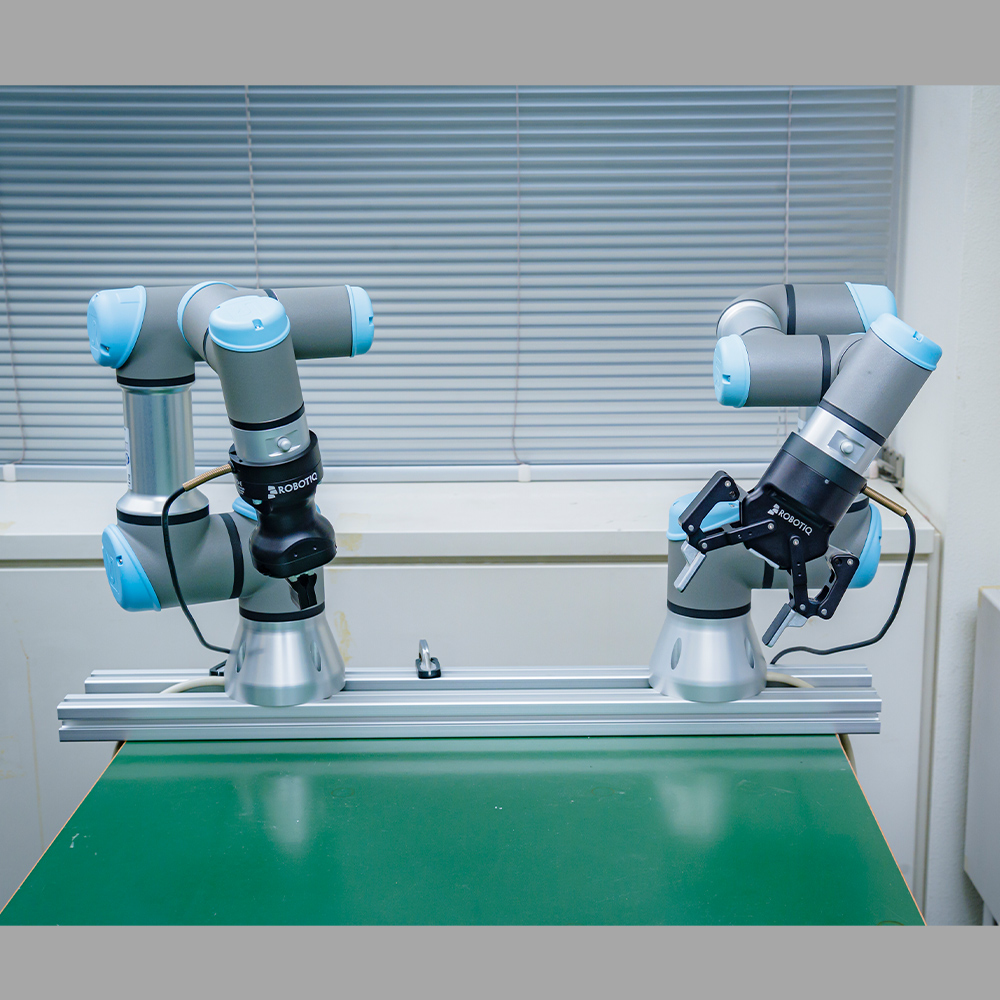
The UR3 robot has six-axis robot arm with a 3kg payload. Its repeatability is ± 0.1 mm, along with speeds up to 1 meter/sec allowing quick precision handling of even microscopically small parts. It has a great balance between control accuracy and velocity and therefore perfectly matches not only pick up/assembling tasks but also safe collaboration with humans. The UR3 robot supports both simple interactions using intuitive tablet interface and programming on scalable open software environment.
(Robot Learning)
Baxter
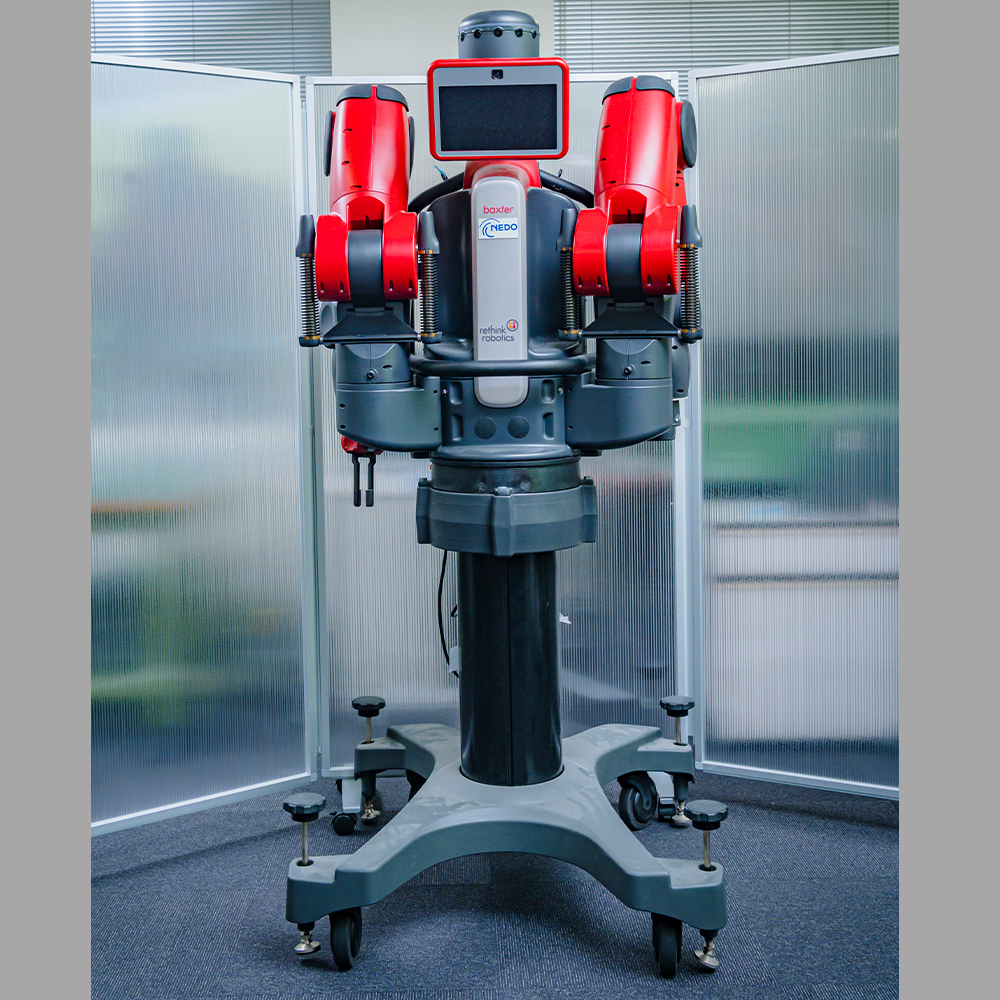

The Baxter is a humanoid, anthropomorphic robot with two 7 DoF arms and state-of-the-art sensing technologies. With force, position, and torque sensors and controllers at every joint, the Baxter robot is suitable for tasks like intelligent assembling and safe collaborative manipulation with humans. Combining with multiple cameras, the Baxter robot can intelligently work in a 3D space while keeping a safe distance to humans to avoid injury.
(Robot Learning)
BioTac
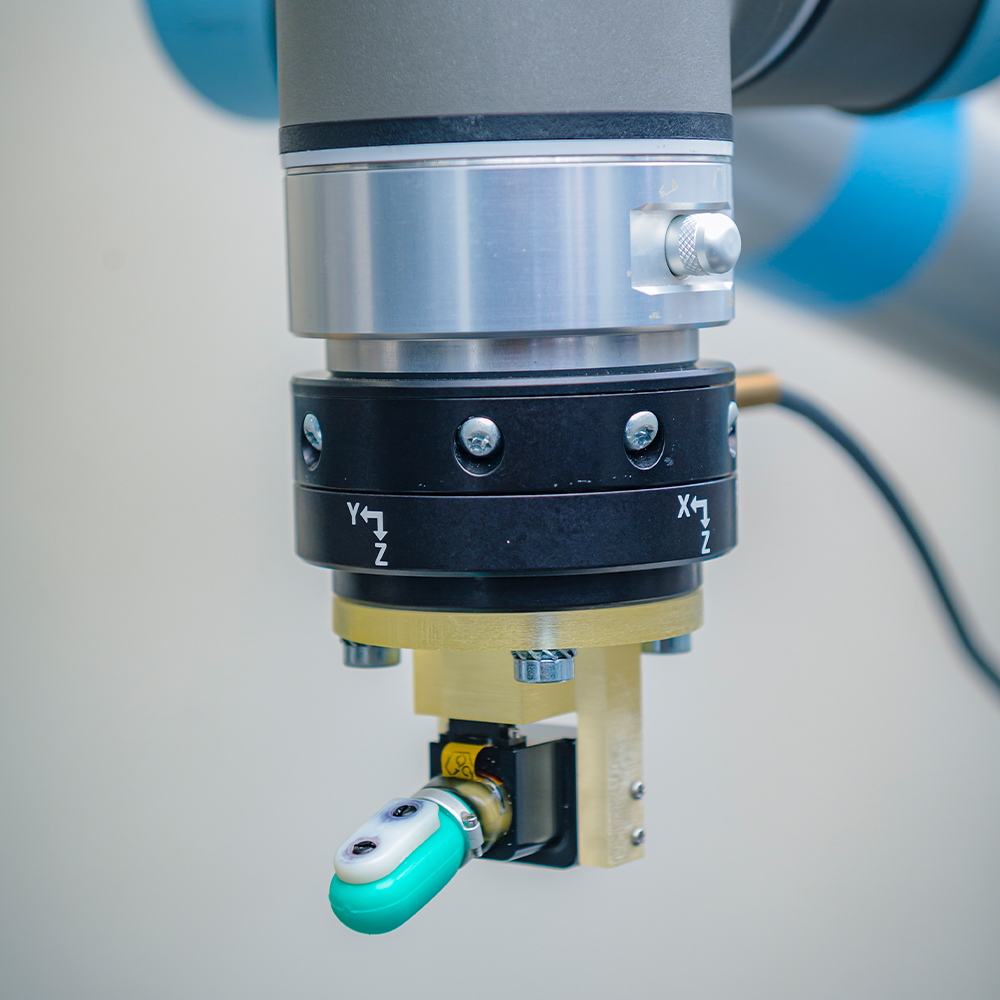
The BioTac is a biomimetic tactile sensor that senses skin sensations similar to a human finger. This sensor can detect three types of tactile information: force, micro-vibration, and heat, with the same level of accuracy as a human finger.
(Robot Learning)
HEBI
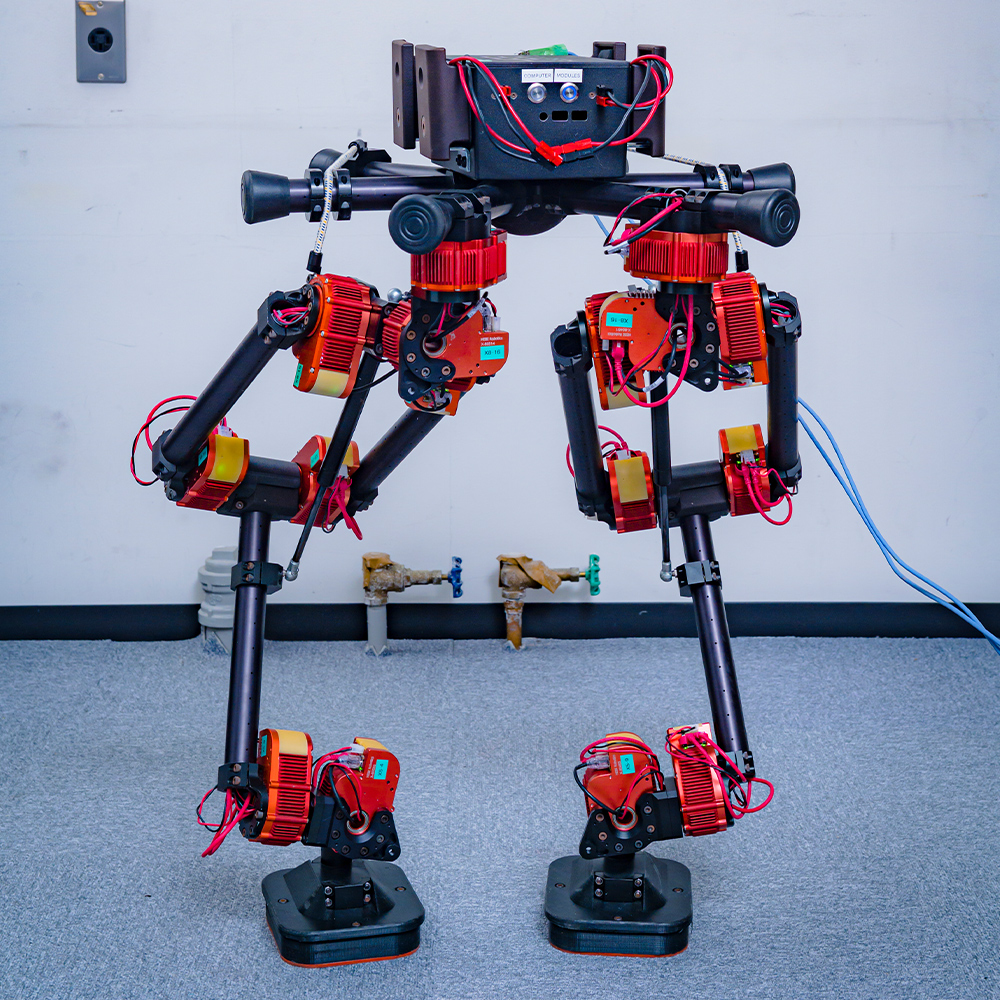
The biped robot is a combination of the HEBI X-Series. Each actuator module is capable of torque control, position control, and velocity control and is also suitable for flexible joint control. Multi-functional actuator modules such as the HEBI X-Series can be used to build multi-joint robots suitable for experiments quickly.
(Robot Learning)
ROBOTIS OP3
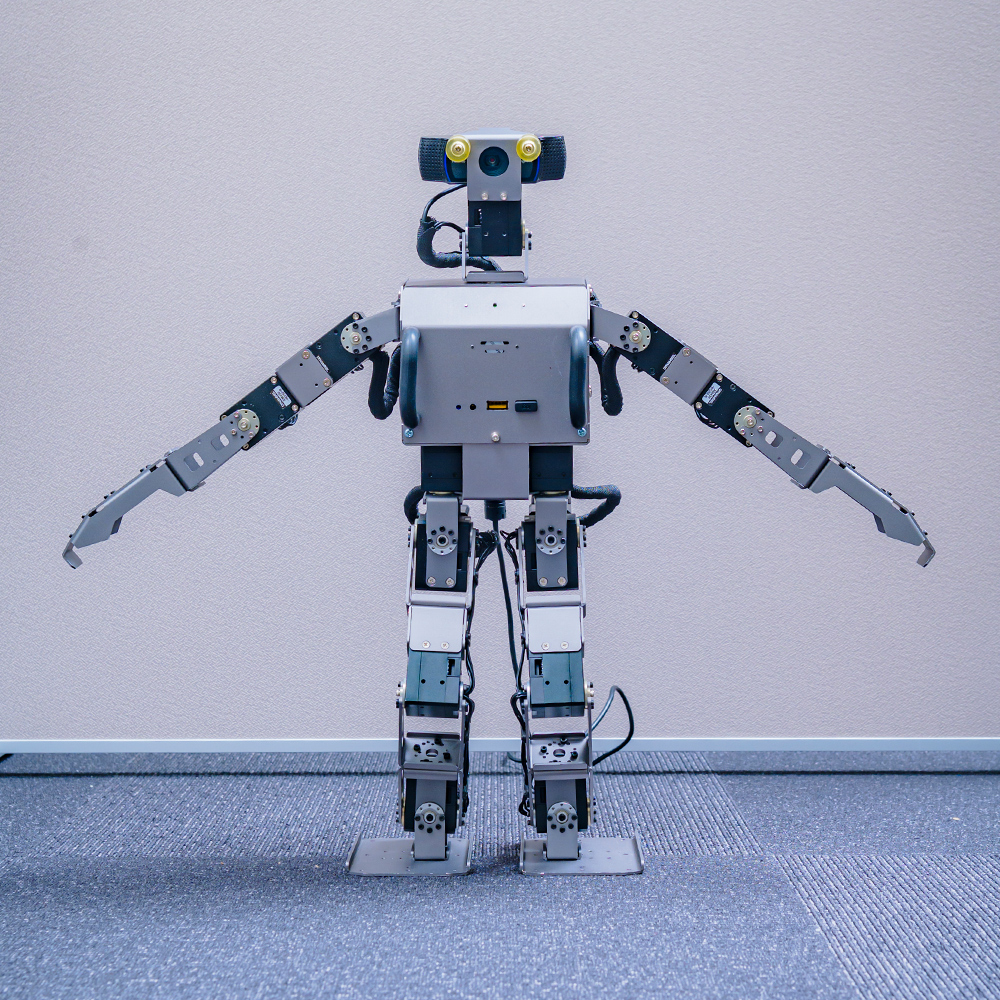
The OP3 is a small 20-axis humanoid robot platform with a total length of 510 mm. This robot includes standard functions such as walking motion and supports simulation by Gazebo. The OP3 robot supports programming in a scalable open software environment.
(Robot Learning)
Unitree A1
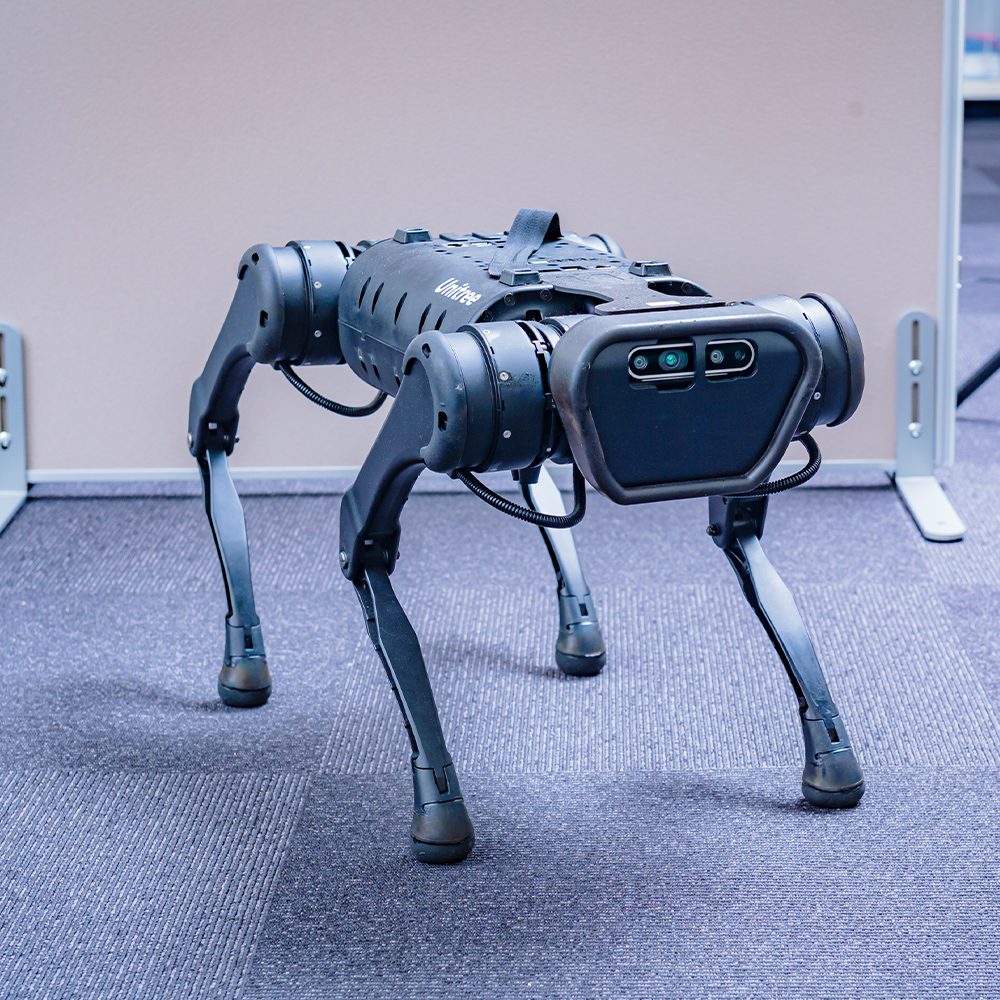

The unitree A1 is an electric quadruped robot with advanced locomotion capabilities. The robot is small in weight (about 13 kg) and agile in movement, with a maximum walking speed of 11.8 km/h, which is about as fast as jogging. A depth sensor is mounted in front of the robot, allowing the development of walking movements suitable for terrain shapes.
(Robot Learning)
Husky + UR5E
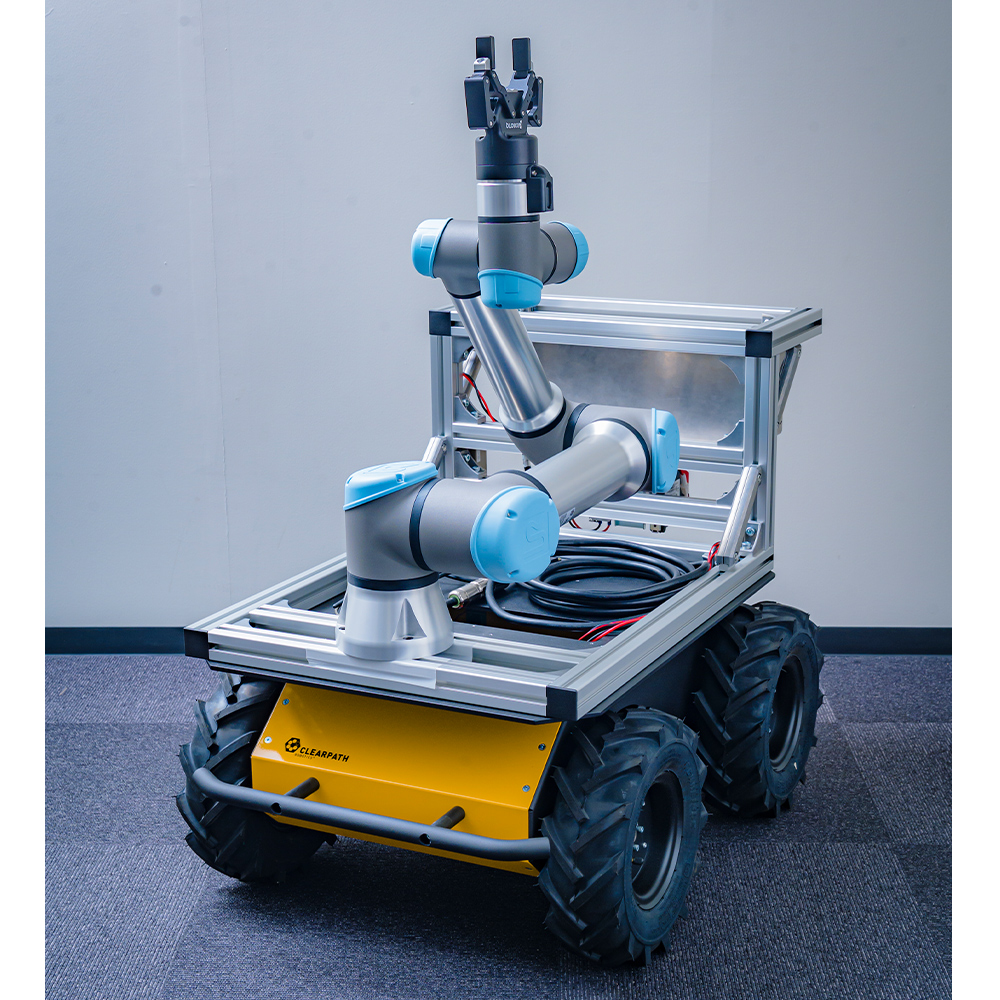

This outdoor mobile manipulator is a four-wheeled robot, Husky, equipped with a 6-axis arm, UR5e. Husky is a high-torque, four-wheel-drive vehicle with a maximum load of 75 kg that can be driven outdoors. The onboard UR5e allows for the manipulation of objects in various locations. This robot is suitable for autonomous transportation tasks indoors and outdoors.
(Robot Learning)
ROBEL
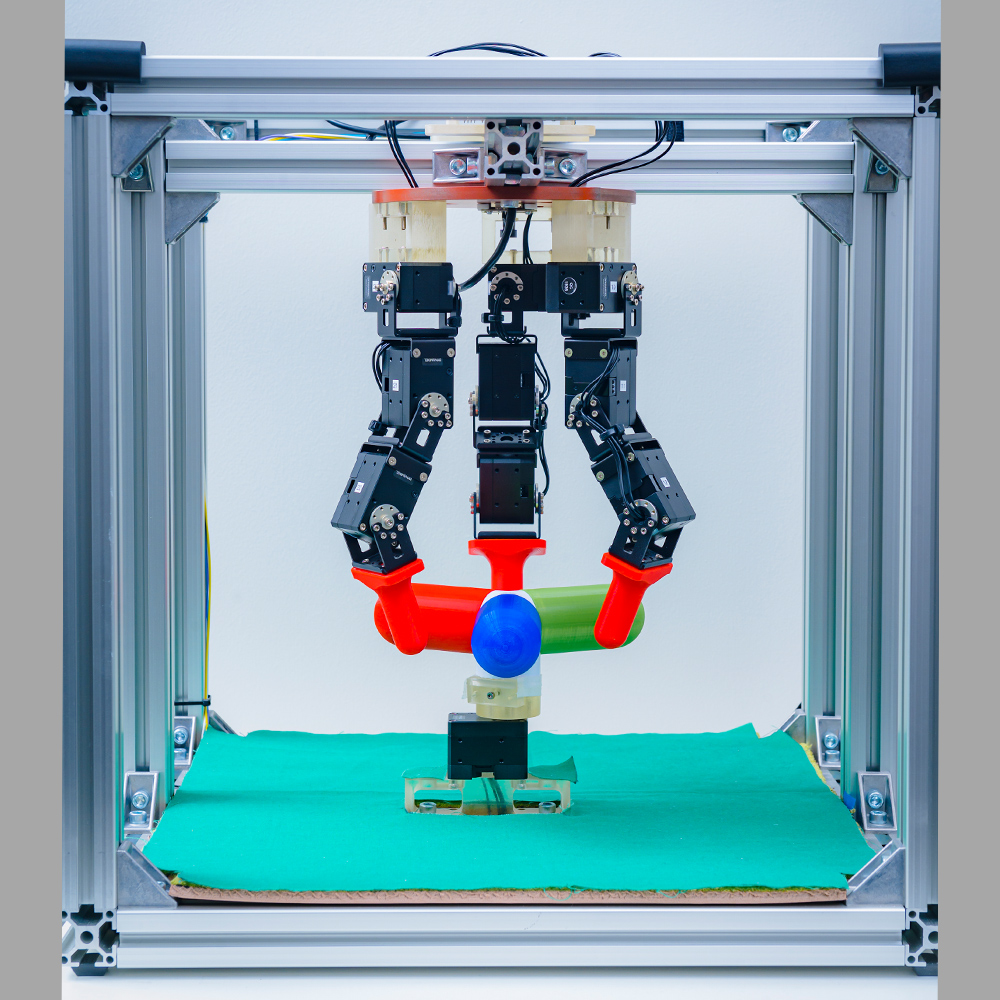
The ROBEL is a robot platform with 9 degrees of freedom. A valve located directly under the robot is manipulated using three fingers. It is a highly sample-efficient benchmark environment because of the easy posture initialization of the robot and valves.
(Robot Learning)